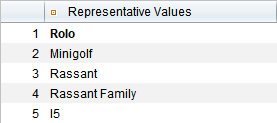What is Data Driven Testing?
Data Driven Testing (DDT) is a test method in which test cases are executed with different test data. Instead of creating a separate test case for each data combination, DDT uses generic test logic. This runs through identical test steps with different values.
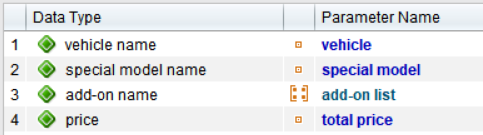
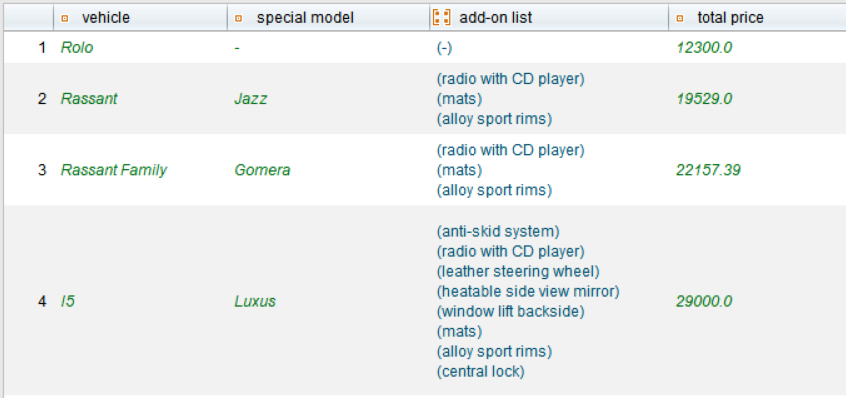
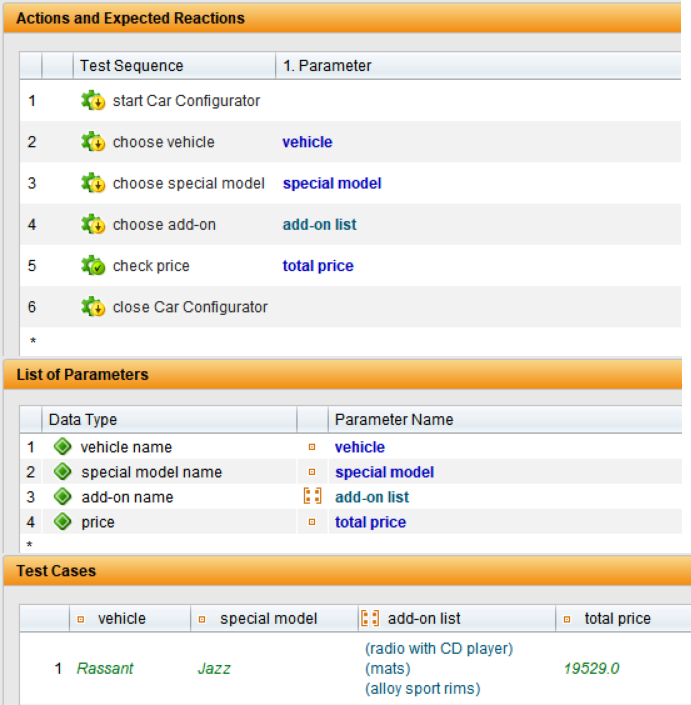
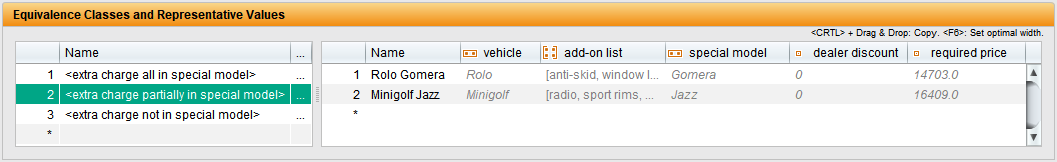
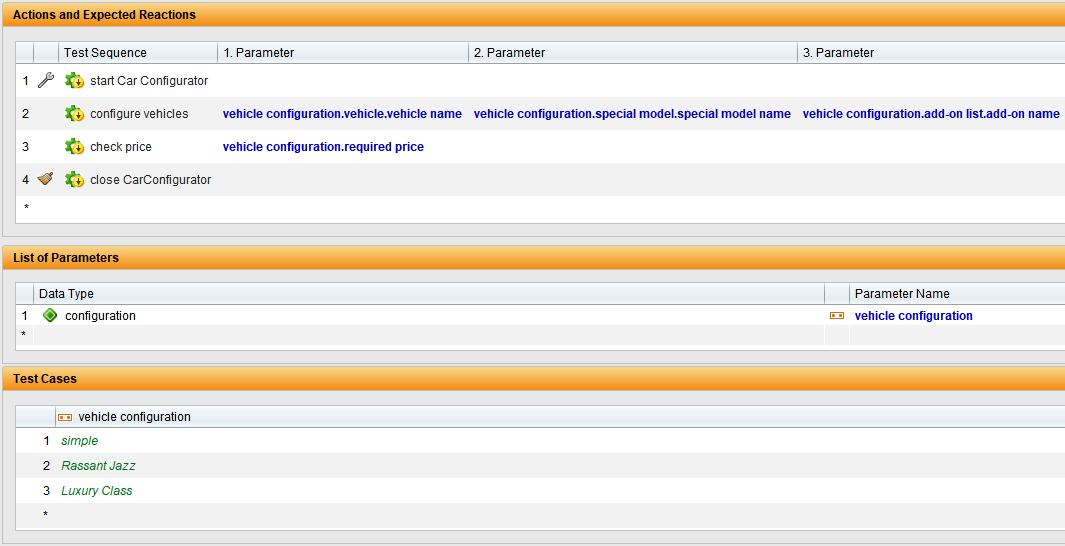
The specific values for inputs and expected results are stored in a data table. Each row in the table corresponds to a test characteristic. This allows tests to be scaled efficiently, test coverage to be increased and redundancies to be avoided. New data combinations are quickly added or updated. Especially in test automation, DDT enables simple and flexible mapping of different scenarios.
Challenges in managing and using test data
Working with test data is associated with various problems, including data management, availability and quality.
The advantages of Data Driven Testing
If the behaviour of a system varies with the same processes when using different data, then Data Driven Testing has a number of advantages:
- Higher test coverage – Separating test logic and test data allows many input values to be tested with the same test sequence. This allows different scenarios to be covered, including limit values and special cases.
- Less maintenance – Changes to the test data do not require any adjustments to the test procedure. New data sets can be easily added or updated without changing the test automation.
- Better error analysis – As each test run is logged with different data, error-prone values can be quickly identified. This makes it easier to analyse the cause and rectify errors in a targeted manner.
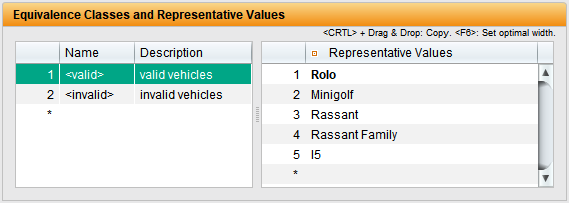
- Avoidance of redundant tests – A targeted selection of data combinations (e.g. via equivalence classes) avoids unnecessary repetitions. This saves time and reduces unnecessary complexity.
- More efficient test design – Centralised management of test data facilitates its reuse. Instead of defining values multiple times, structured data records can be used specifically for tests.
When is Data Driven Testing recommended?
Data Driven Testing is particularly effective when many data combinations need to be tested or test cases are reused. For data driven applications in particular, DDT reduces manual effort, improves test coverage and increases efficiency.
If test cases are heavily dependent on external test data, DDT enables simple management and scaling. The preparation of test data for inputs or special compilations, such as waybills or insurance forms, simplifies both specification and test execution.
Data Driven Testing is particularly powerful in combination with Keyword Driven Testing.
How does Data Driven Testing work with TestBench?
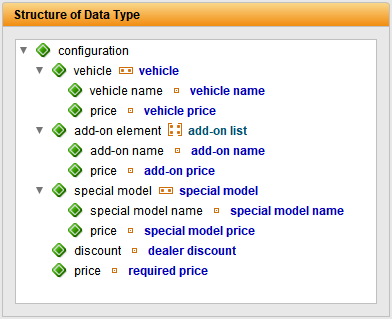
TestBench manages test data in a structured and contextualised way. To make this possible, data is stored in separate data types. This structure improves management and makes it easier to access the required values.
Advantages of Data Driven Testing in Manual Testing
Data-driven testing not only increases the efficiency of test automation, but also improves manual tests.

Faster test execution
Repeated test sequences can be executed more quickly as they do not have to be re-read each time.

Reduced susceptibility to errors
Instead of typing in values manually, existing data records can simply be run through. In the TestBench, data can also be pasted directly from the clipboard.

Increased test efficiency
More scenarios can be covered by a targeted variation of test data – without additional manual effort.
Details on test execution can be found here and in the blog post ‘Less effort, more efficiency: the iTORX assistant’.