What is Variant Management?
Variant management is a central component of product development, especially in industries where numerous individual product variants are based on a common platform. It deals with the efficient management of products that are largely identical but vary in specific features. These differences can take the form of equipment options, functions or other individual adaptations based on a common product platform. The aim of variant management is to control and test these differences, known as variant specifics, in a targeted manner. This ensures that each variant has the required quality and functionality. This is necessary in order to guarantee high product quality. Precise coordination is essential in order to control complexity and avoid efficiency losses.
Challenges in testing variant-rich systems

- Redundancy and efficiency losses
Tests for common functionalities often lead to superfluous work. - Insufficient test availability
Some variants are not tested in time or not tested at all. - Complex test data management
Each product variant requires specific data, which makes administration more difficult. - Change detection and tracking
Cross-variant changes are difficult to track. - Test case control
Determining the right number of test cases for each product variant is challenging. - Lack of standardization
Without standardized processes, inconsistencies arise.
How does variant management work with TestBench?
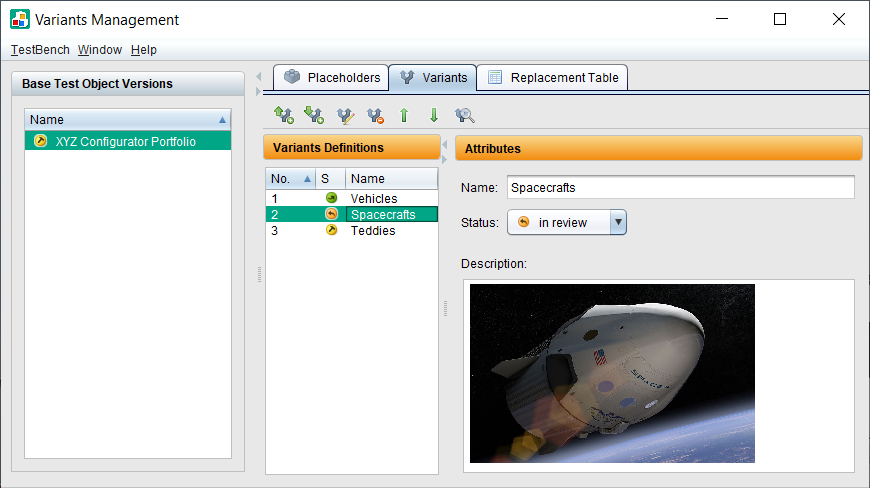
TestBench offers effective variant management that minimizes testing effort. The system enables low-redundancy testing by creating a basic test object version. This version contains test specifications that apply to all variants of a product line. Individual variant versions are derived from this base version, each of which takes into account the common and specific requirements and tests of a product variant.

Detailed functions in variant management
In TestBench’s variant management, test specifications are precisely tailored to the respective product variant. The following functions are available:
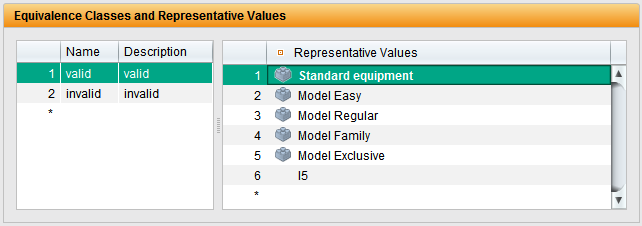
- Definition of validity: Determine which tests apply to which product variant.
- Adaptation of test sequences: Design test sequences to be variant-dependent.
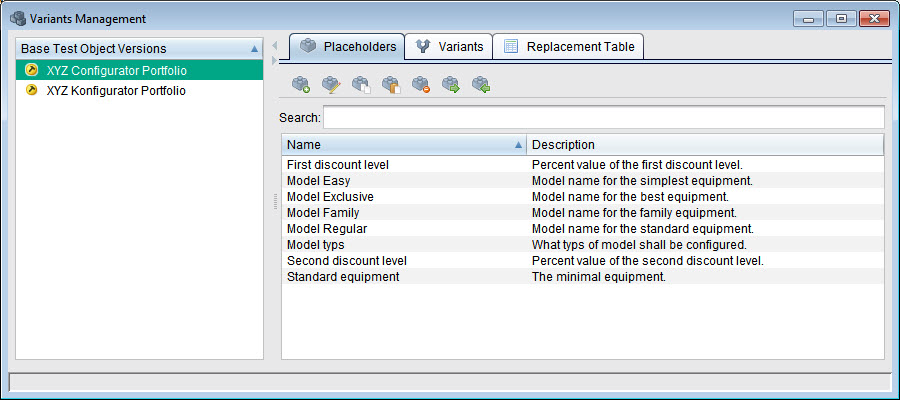
- Test data management: Define parameters and test data for each product variant.
A variant is derived in two steps. First, the number of tests is adapted to the variants. Variant markers help to assign the respective test elements. Then the test data is specifically adapted using placeholders. These placeholders allow individual values to be defined for each variant.
All advantages at a glance